
Irinos Measurement System
As shown in the following figure, the physical connection between the Irinos-System and the PC is made via an Ethernet cable. Typically it has an M12 connector for the Irinos Master-Box and a RJ45 connector for the PC.
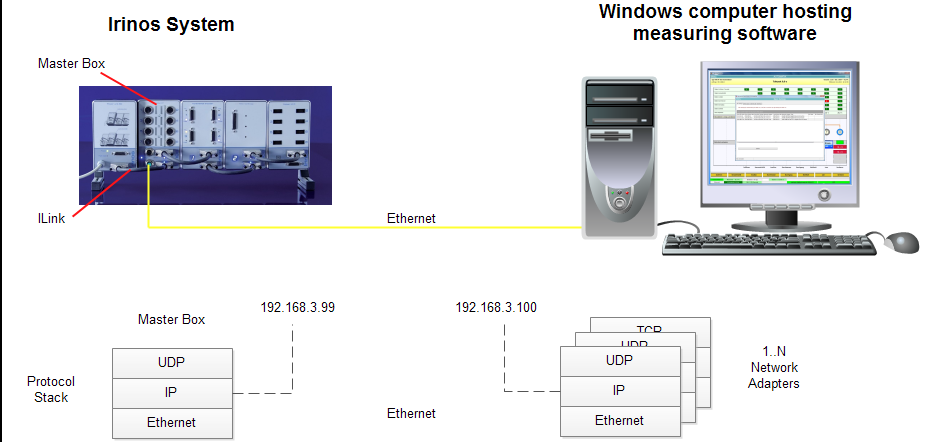
System overview
The communication itself is based on the commonly used UDP and IP protocols.
Basically, network devices need to be configured before a communication link can be established. In particular, IP settings are mandatory on both sides of the communication link. Both, the Irinos Master-Box and the host computer need to be equipped at least with an IP address, and a subnet mask. In some cases a default gateway is configured as well.
If set manually, IP settings on the Windows host are done in the Windows Control Panel. For the Irinos system the Irinos Tool is provided, which enables the user to execute basic network settings. Additionally it contains a broad set of utilities, which support putting the Irinos system into operation. A detailed description of the Irinos Tool is given in chapter 3.2.
Manual IP setting, however, is often cumbersome and may not necessarily lead to established communication links. A better choice is DCHP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), a network protocol which handles this task more reliable and user-friendly. DCHP basically knows two roles: A DHCP server, who is responsible for handling a pool of IP addresses, and a DHCP client, who queries the server for an IP address.
The Irinos Master-Box provides such a DHCP server. The DCHP Server is active by factory defaults, so the task of providing proper IP settings can fully be delegated to the DHCP function.
As a prerequisite, the network setting on the Windows computer need to be set accordingly.
